- Last Updated:
Technical SEO is critical for SaaS websites’ web accessibility as it focuses on optimizing the underlying technical aspects to improve search engine visibility, user experience, and site performance. For SaaS businesses, proper technical SEO ensures that search engines efficiently crawl, index, and rank your site which is essential for attracting potential customers and maintaining competitive visibility in the market. Implementing best practices ensures that your SaaS website is accessible to both users and search engines thereby boosting its ability to attract and retain customers.
The benefits of technical SEO optimization are optimizing site speed, enhancing user experience, improving security, crawling websites, improving SEO rankings, removing duplicate content, and supporting easy navigation. The fundamentals of technical SEO audits verify your preferred domain, crawlability essentials, indexability essentials, renderability essentials, rankability essentials, and clickability essentials.
This ultimate guide provides in-depth details of a technical SEO guide for saas, the benefits of technical SEO, the fundamentals of technical SEO, and everything in between.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Technical SEO?
Technical SEO is an SEO technique that involves optimizing web accessibility of a website to improve its crawling, indexing, and overall performance in search engines. For a SaaS website, improving web accessibility enhances crawl budget efficiency, reduces load time, and ensures proper indexing of all important pages which leads to better search engine rankings, improved user experience, and increased organic traffic.
Does Technical SEO Work for SaaS Websites?
Yes, technical SEO works effectively for a SaaS website. Implementing technical SEO practices, such as optimizing website speed, ensuring mobile optimization, and securing an SSL certificate, enhances the overall performance and security of SaaS platforms that contribute to better user experience, higher search engine rankings, and increased visibility, making technical SEO a vital component for SaaS website success.
Why Technical SEO is Important for SaaS SEO?
Technical SEO is important for SaaS SEO because it supports search engine optimization efforts of a SaaS website by improving web accessibility to ensure the website is effectively crawled, indexed, and ranked by search engines. This is why technical SEO is a significant part of overall SaaS SEO strategy.
Technical SEO also contributes to an enhanced user experience by improving website performance, making sites mobile-friendly, and ensuring fast page load times. Technical SEO also addresses issues like broken links and duplicate content, which impact indexing and better rankings and significantly increase organic traffic, improve your site’s visibility, and ultimately achieve better search engine results.
Is Technical SEO Better Than Off-Page SEO?
Technical SEO and Off-Page SEO serve different but complementary purposes in a website’s overall search engine optimization strategy, making it difficult to determine which one is inherently better.
Off-page SEO focuses on activities outside the website that influence search engine rankings. The primary aspect of off-page SEO is building high-quality backlinks from authoritative websites. Still, it also includes social media marketing, brand mentions, and influencer outreach off-page SEO signals to search engines that the website is reputable, popular, and authoritative. Earning backlinks from trusted domains significantly boosts a site’s credibility and authority, contributing to higher rankings.
Technical SEO refers to the optimization efforts applied directly to the structure and backend of a website. It involves improving site speed, mobile-friendliness, crawlability, indexing, security (such as HTTPS), and XML sitemaps. Technical SEO ensures that search engines effectively crawl, index, and understand a website’s content, which is fundamental for search rankings. A well-optimized technical SEO foundation allows the website to load faster, function smoothly on all devices, and remain secure, which directly impacts user experience and search engine trust.
Is Technical SEO Better Than On-Page?
Technical SEO and On-Page SEO are both critical to a website’s overall success, with neither being inherently better than the other.
On-page SEO is about optimizing the content and structure of individual web pages to make them more relevant and engaging for both users and search engines which includes optimizing meta tags, headings, keyword usage, internal links, and overall content quality. On-page SEO ensures that each page is informative, well-organized, and directly related to search queries and also enhances user engagement by making the content easy to read, relevant, and useful. Good on-page SEO provides immediate value to users and signals to search engines that the content is worth ranking.
Technical SEO focuses on the infrastructure and backend of a website. It involves ensuring that a website is crawlable, indexable, secure, and fast-loading. Elements like page speed, mobile optimization, structured data, and XML sitemaps are central to technical SEO. These aspects ensure that search engines effectively access and interpret your site. Without strong technical SEO, even the best content may not rank well due to slow speeds, broken links, or other technical issues that negatively impact user experience and search engine trust.
What are the Benefits of Technical SEO Optimization?
The benefits of technical SEO optimization are optimizing site speed, enhancing user experience, improving security, crawling websites, improving SEO rankings, removing duplicate content, supporting easy navigation, increasing organic traffic, facilitating indexing, identifying broken links, reducing bounce rate, and increasing click-through rates.
Here are the key benefits of technical SEO:
Optimizes Site speed
Site speed is a webpage’s loading time. The faster load times significantly enhance the user experience by reducing page load times which in turn minimizes bounce rates and keeps visitors engaged. Improved site speed leads to a better overall user experience, fostering increased engagement and higher satisfaction levels.
Enhances user experience
User experience (UX) is vital as it directly impacts how visitors interact with your site, influencing their overall satisfaction and likelihood of returning. A user-friendly design ensures that visitors navigate your site easily, while page speed optimization keeps the experience smooth and frustration-free.
Improves Security
Secure Browsing involves using protocols and practices that ensure a safe and private online experience for users. Implementing HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) enhances security by encrypting data transmitted between the user’s browser and the web server, protecting sensitive information from interception or tampering helps safeguard user data but also builds trust, as visitors are more likely to engage with a site that displays the padlock icon associated with HTTPS. Additionally, HTTPS improves search engine rankings, as search engines prioritize secure sites in their results.
Facilitates Crawlers
A web crawler, also known as a spider or bot, is an automated program used by search engines to systematically browse and analyze websites. Crawling refers to the process of systematically visiting web pages to discover new or updated content. Once a page is crawled, the crawler retrieves the page’s content, including text, images, and other media. content is then indexed, which involves organizing and storing the information in a way that allows search engines to quickly retrieve it when users perform searches. Finally, the crawler may render the page to understand how it appears and functions, ensuring that dynamic content or scripts are appropriately handled and included in the search index.
Improves SEO Ranking
Higher SEO ranking involves optimizing various elements of a site, such as improving page speed, ensuring mobile-friendliness, and implementing proper indexing practices. These optimizations enhance the overall performance and usability of a website, making it easier for search engines to crawl and understand the content. Search engines are more likely to rank the site higher in search results, increasing its chances of being seen by potential visitors and driving more organic traffic to the site.
Removes Duplicate content
Duplicate content leads to lower search engine rankings and confusion over which version of a page should be indexed which may also dilute the website’s authority and hinder the effectiveness of SEO efforts. Technical SEO helps remove duplicate content by implementing strategies such as using canonical tags to specify the preferred version of a page, setting up proper redirects, and ensuring that unique content is provided across all pages improves crawl efficiency, enhances user experience by reducing the chances of encountering duplicate pages, and increases the site’s authority by consolidating ranking signals.
Supports Easy Navigation
Easy navigation is crucial for a positive user experience, as it allows visitors to find the information they need quickly and efficiently, leading to higher satisfaction and retention. Good navigation enhances user experience by providing a clear structure and intuitive paths through the site. Technical SEO supports easy navigation by improving the website’s structure, such as implementing clear menu systems, breadcrumb trails, and internal linking. Improved navigation boosts engagement by making it easier for users to explore and interact with the site, and supports higher conversion rates by streamlining the process of finding and acting on key information or offers.
Increases Organic Traffic
Technical SEO boosts organic traffic by optimizing various elements of a website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results. Properly implemented technical SEO also helps prevent issues like broken links and duplicate content, which hinder search engine rankings. Additionally, optimizing metadata and improving site architecture make your pages more appealing to both search engines and users, ultimately leading to higher organic traffic as your site ranks better and attracts more visitors from search engine results.
Facilitates Indexing
Indexing is the process by which search engines analyze and store information from web pages to include them in their database, allowing users to find and access content through search results. Technical SEO facilitates indexing by ensuring that search engines efficiently crawl and understand the content of a website creating and submitting XML sitemaps, optimizing robots.txt files to guide crawlers, fixing broken links, and using canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues. Additionally, improving site speed and mobile responsiveness helps search engines access and index pages more effectively, leading to better visibility in search results.
Identifies Broken links
Broken links refer to URLs that lead to pages that no longer exist or have been moved, often resulting in a 404 error. These errors occur with both inbound links (links from other sites pointing to your pages) and outbound links (links from your site pointing to external pages). The side effects of broken links include a poor user experience, loss of credibility, reduced SEO value due to disrupted link equity, and potential negative impacts on search engine rankings. Technical SEO helps identify 404 errors by using tools and techniques that monitor and analyze your site’s links employing site auditing tools for broken links, analyzing server response codes to detect 404 errors, and using Google Search Console to identify and fix issues reported by search engines.
Reduces Bounce Rates
Bounce rate refers to the percentage of visitors who leave a website after viewing only one page, without interacting further. A high bounce rate often indicates that visitors did not find what they were looking for or had a poor user experience. Technical SEO helps reduce bounce rates by optimizing various aspects of a website. Optimized page speed ensures that pages load quickly, preventing users from leaving out of frustration. Clean navigation makes it easy for visitors to find relevant content and move through the site effortlessly.
Increases Click-Through Rates (CTR)
Click-Through Rate (CTR) measures the percentage of users who click on a link or ad after seeing it. It is a key metric for evaluating the effectiveness of a website’s visibility and appeal in search engine results. Technical SEO helps increase CTR by enhancing listings in search engine results pages (SERPs) with rich snippets and better descriptions. Implementing structured data enables rich snippets that provide additional information such as star ratings, reviews, or pricing, making the listing more attractive and informative. Crafting compelling meta descriptions also improves the appeal of search results, encouraging users to click through to your site.
What are the Fundamentals of Technical SEO Audits?
The fundamentals of technical SEO audits to improve web accessibility include verifying your preferred domain, crawlability essentials, indexability essentials, renderability essentials, rankability essentials, and clickability essentials.
The following image shows the fundamentals of technical SEO audits:
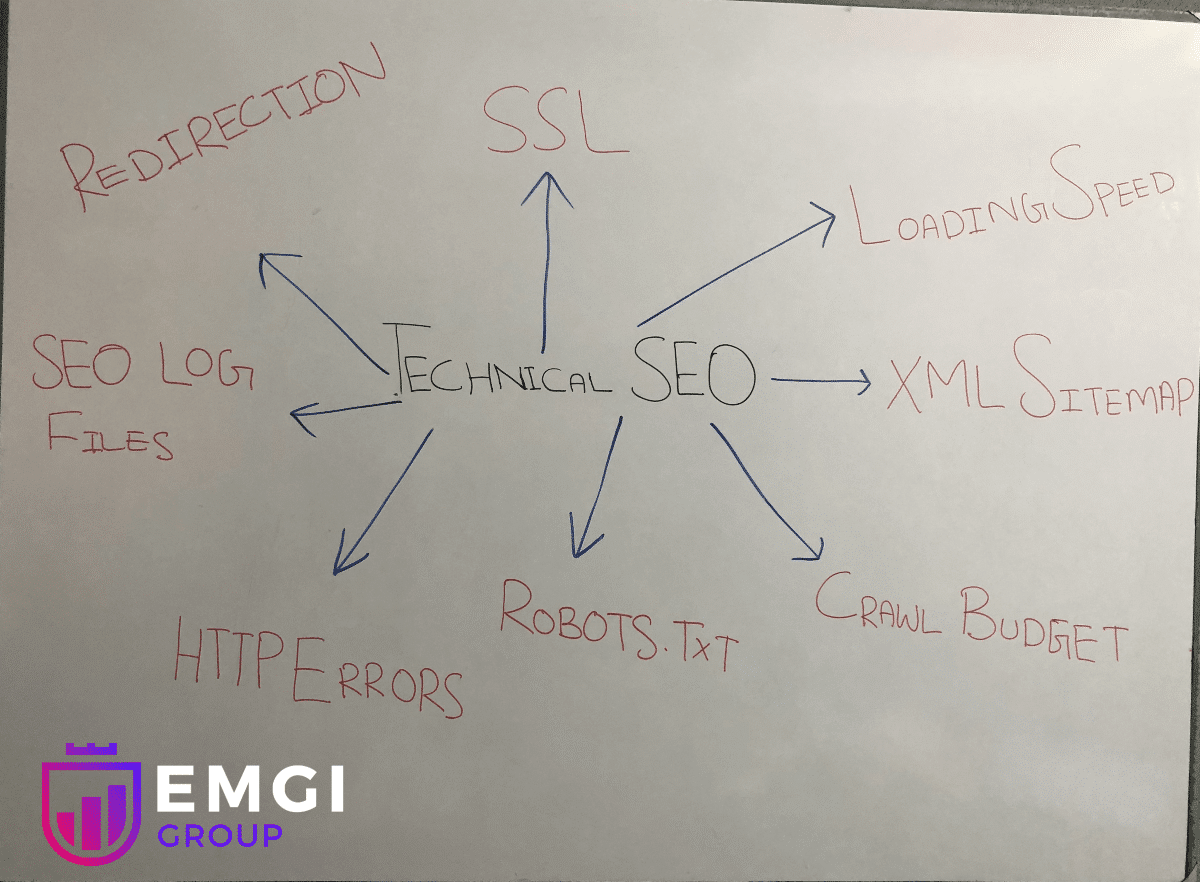
Here are the key fundamentals of a technical SEO audit:
Verify Your Preferred Domain
Domain Verification involves confirming that you have ownership and control over a domain name. ensures that the domain is correctly set up and secure, and allows you to manage its settings, such as DNS records and security configurations. Verifying your domain is crucial for ensuring that your website and its associated services are secure and properly configured. It helps protect against unauthorized changes and ensures that you have control over your domain’s DNS settings, email configurations, and other critical aspects.
How to Verify Your Domain for Security:
- Create a TXT or CNAME record in your domain’s DNS settings provided by the verification service (e.g., Google Search Console). record helps confirm that you have control over the domain.
- Some verification services provide an HTML file that you need to upload to the root directory of your domain. Accessing files through your browser verifies your ownership.
- For some services, you verify your domain by receiving and responding to a verification email sent to a domain-associated email address (e.g., admin@yourdomain.com).
- Ensure your domain has a valid SSL/TLS certificate, which encrypts data exchanged between your site and users, further confirming the domain’s security.
Implement Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is a security protocol that encrypts data transmitted between a user’s browser and a web server, ensuring secure and private communication. Implementing SSL is crucial for protecting sensitive information, such as login credentials and personal details, from interception and unauthorized access. It also helps build trust with users and improves search engine rankings.
Enhance Page Loading Speed
Page Loading Speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a web page to fully display its content to users after they request it. Optimizing page loading speed is vital for technical SEO as it directly affects user experience and site performance. Faster loading pages result in quicker access to content, improved usability, and higher user retention. Search engines, like Google, prioritize fast-loading websites in their rankings, so optimizing speed leads to better visibility and higher search engine rankings.
How It Works for Technical SEO:
- Compressing and resizing images reduces their file size without significantly affecting quality, leading to faster page loads. Tools like image compressors and responsive images help in achieving this.
- Storing frequently used resources, such as images and scripts, in a user’s browser cache reduces the need to re-download them with each visit. speeds up loading times for returning users.
- Reducing the size and number of JavaScript and CSS files through minification and combining them into fewer files decreases the amount of data that needs to be processed and loaded, enhancing page speed.
Crawlability Essentials
Crawling is the process by which search engines use automated bots, known as crawlers or spiders, to systematically browse and index the pages of a website.
Crawlability is crucial for SaaS websites as it ensures that search engine bots access and index all relevant pages, which directly affects visibility in search engine results. For SaaS platforms, effective crawling enables the search engine to understand and rank the site’s content, features, and services, making it easier for potential customers to find the site. Improved crawlability enhances the chances of appearing in relevant search queries, driving organic traffic, and gaining new users.
Here are the crawlability essentials:
Generate an XML Sitemap
XML Sitemap is a file that provides search engines with a structured list of all the important pages on a website and helps search engines understand the site’s structure, prioritize pages for crawling, and index them more efficiently. Generating an XML sitemap facilitates efficient crawling and indexing by search engines, ensuring that all important pages are discovered and considered for ranking. An XML sitemap helps search engines understand the site’s structure, prioritize the most significant pages, and detect updates or new content promptly. For larger websites or those with complex structures, having a sitemap ensures that even deeply nested pages are not overlooked.
How to Generate an XML Sitemap:
- Utilize online tools or plugins, such as Google XML Sitemaps for WordPress or Screaming Frog SEO Spider, to automatically generate an XML sitemap based on your website’s structure.
- For manual generation, create an XML file using a text editor with the proper XML format, listing all important URLs along with metadata like the last modification date and frequency of changes.
- created, upload the XML sitemap to the root directory of your website, and submit it to search engines through tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools to ensure they are aware of and crawl the sitemap.
Optimize Your Crawl Budget
Crawl Budget refers to the number of pages a search engine crawler will visit and index from a website within a specific timeframe and influenced by the site’s size, health, and authority, and helps determine how often and how deeply a search engine bot will crawl your site. Optimizing the crawl budget prevents valuable pages from being overlooked due to crawler inefficiencies, improving the likelihood that these pages will appear in search results. optimization helps enhance the site’s visibility, improve search engine rankings, and ensure that updates or new content are quickly recognized and indexed.
How to Optimize Crawl Budget:
- Use tools like Google Search Console to identify and correct crawl errors (e.g., 404 errors) that waste the crawl budget on broken links.
- Ensure your site has a clear, logical structure with well-defined internal linking to guide crawlers to important pages efficiently.
- Manage crawler access by blocking non-essential pages with robots.txt or meta tags to focus the crawl budget on high-priority content.
- Faster-loading pages be crawled more efficiently. Optimize load times to ensure crawlers access more pages in the same timeframe.
- Regularly updating high-quality content signals to crawlers that the site is active and valuable, encouraging more frequent visits.
Improve Site Architecture
Site Architecture refers to the structural layout of a website, including the organization and hierarchy of its pages and how they are linked together. Improving site architecture enhances user experience by making it easier for visitors to find and navigate content, thereby increasing engagement and satisfaction. For search engines, a well-organized site structure facilitates efficient crawling and indexing, ensuring that important pages are discovered and ranked effectively. Additionally, a solid site architecture simplifies site management and content updates, making it easier to maintain and expand the website as needed.
How to Check Site Architecture:
- Examine the website’s navigation menus and URL structure to ensure they logically group related content and allow users to easily find and access information.
- Analyze XML and HTML sitemaps to understand the site’s organization and how pages are connected. Tools like Google Search Console help in reviewing these sitemaps.
- Use web crawling tools, such as Screaming Frog or Sitebulb, to simulate how search engines crawl your site, identifying any issues with page access or link structure.
- Conduct usability testing to see how easily users navigate through the site and locate content, which reveals areas where the architecture might need improvement.
Establish a Clear URL Structure
URL Structure refers to the format and hierarchy of URLs on a website, including how pages are named and organized within the domain. A logical and descriptive URL structure enhances usability by making it easier for visitors to understand the content of a page and navigate the site. For search engines, clear URLs improve crawlability and indexing, as they provide a straightforward way to understand the site’s hierarchy and content. Well-structured URLs also contribute to better search engine rankings by incorporating relevant keywords and reducing the likelihood of duplicate content issues.
How to Establish a Clear URL Structure:
- Ensure URLs include relevant keywords that describe the page content, making them more informative and relevant to search queries.
- Keep URLs short, simple, and consistent across the site. Avoid unnecessary parameters or complex strings that confuse users and search engines.
- Structure URLs to reflect the site’s hierarchy, with categories and subcategories delineated. For example, use example.com/category/subcategory/page to show the relationship between pages.
- Prefer static URLs over dynamic ones (e.g., example.com/product-123 vs. example.com/product?id=123) to ensure cleaner, more user-friendly URLs.
- Separate words in URLs with hyphens rather than underscores, as hyphens are more easily interpreted by search engines.
Configure robots.txt
robots.txt is a file placed in the root directory of a website that provides directives to web crawlers about which pages or sections of the site should be crawled or avoided. Configuring robots.txt prevents search engines from irrelevant indexing pages or duplicates, such as admin panels or staging sites, which improve the overall quality of the indexed content and avoid dilution of page authority. Additionally, robots.txt guides bots on the proper paths to crawl, ensuring that critical pages are indexed while protecting sensitive or non-essential content.
Incorporate Breadcrumb Menus
Breadcrumbs are a navigational element on a website that shows users their current location within the site’s hierarchy and are displayed as a horizontal list of links separated by symbols (like arrows or slashes), breadcrumbs provide a trail back to the homepage or higher-level pages. For search engines, breadcrumbs help establish a clear site structure and hierarchy, which improves indexing and ranking. They also contribute to better site organization by visually representing the relationship between different pages. Breadcrumbs also enhance SEO by providing more internal links which helps distribute page authority throughout the site and facilitates better crawling by search engines.
Implement Pagination
Pagination is a technique used to divide large sets of content into smaller, manageable pages, often seen in search results, article lists, or product catalogs. Implementing pagination improves page load times and site performance by reducing the amount of content loaded at once. From an SEO perspective, proper pagination helps search engines understand the structure of content across multiple pages, which aids in indexing and ranking. It also prevents issues with duplicate content by ensuring that each paginated page is distinct and optimized.
Review Your SEO Log Files
SEO Log Files are files generated by a website’s server that record various activities and interactions between web crawlers and the site. These logs include details such as crawl requests, response codes, and the frequency and timing of crawler visits. Reviewing SEO log files reveals which pages are being crawled, the frequency of crawls, and any errors or redirects encountered by bots which helps in diagnosing crawl issues, optimizing site performance, and improving the efficiency of search engine indexing.
Indexability Essentials
Indexability refers to the ability of search engines to access, crawl, and index a website’s pages so that they appear in search engine results. For a page to be indexable, it must be free from barriers that prevent search engines from reading and understanding its content, such as incorrect robots.txt settings or meta tags. If pages are not indexable, they won’t appear in search results, leading to missed opportunities for organic traffic and lower search engine rankings. Proper indexability allows search engines to effectively crawl and include your content in their databases, which is essential for achieving good visibility and driving traffic to your site.
Here are the essential steps to improve and maintain your site’s indexability:
Ensure Easy Web Accessibility
Web accessibility is the practice of ensuring there are no barriers that prevent interaction with, or access to, websites on the World Wide Web by people with physical disabilities, situational disabilities, and socio-economic restrictions on bandwidth and speed. Search Bots are automated programs used by search engines to crawl and index web pages. They navigate the internet, follow links, and analyze page content to understand and categorize it for search engine results.
Your website should have a clear and functional structure that allows bots to easily follow links and reach all important content. If search bots are unable to crawl or index your pages, those pages won’t appear in search engine results, limiting your site’s reach and potential traffic. Accessible pages allow search engines to properly understand, categorize, and rank your content, which is essential for achieving good search engine rankings and attracting organic traffic.
Eliminate Duplicate Content
Duplicate Content refers to blocks of content that are identical or very similar across multiple web pages, whether within the same site or across different sites. Eliminating duplicate content is vital for maintaining effective SEO. Duplicate content dilutes page authority, confuses search engines, and results in lower rankings or penalties. It also leads to a wasted crawl budget, as search engines may spend time indexing duplicate pages instead of focusing on unique and valuable content.
Steps to Eliminate Duplicate Content:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify duplicate content across your site.
- Add canonical tags to the head section of your HTML to indicate the preferred version of a page to search engines. helps prevent duplicate content issues by directing search engines to the original content.
- For duplicate pages that should not exist, use 301 redirects to point them to the preferred version, consolidating page authority.
- Adjust URL parameters that generate duplicate content, ensuring unique content paths or using URL parameter handling tools in Google Search Console.
- Merge similar content into a single comprehensive page, or use rel=canonical tags to specify the main source.
- Monitor for and address content scraping or syndication issues by setting proper permissions and using content protection measures.
Evaluate Your Redirects
Redirects are mechanisms used to send users and search engines from one URL to another. They are commonly used when content has been moved or when URLs have changed. Evaluating redirects is crucial for maintaining a seamless user experience and effective SEO. Poorly managed redirects lead to broken links, slow page load times, and ineffective SEO if they create redirect chains or loops. Proper evaluation ensures that users are directed to the correct content without interruptions and that search engines accurately index and rank the appropriate pages.
How to Evaluate Your Redirects:
- Use tools like Screaming Frog, Google Search Console, or Sitebulb to identify and review all existing redirects on your site.
- Ensure that permanent redirects (301) are used for pages that have been moved permanently, and temporary redirects (302 or 307) are used for temporary changes.
- Evaluate if redirects are creating chains (multiple redirects from one URL to another) and resolve them to avoid unnecessary steps.
- Manually test redirects to ensure they correctly lead to the intended destination without errors.
- Track metrics such as user experience, page load times, and SEO impact to assess the effectiveness of your redirects.
Assess Mobile Responsiveness
Mobile Responsiveness refers to a website’s ability to adapt its layout and content to provide an optimal viewing experience across a range of devices, including smartphones and tablets. Assessing mobile responsiveness is critical because a significant portion of web traffic comes from mobile devices. A responsive design ensures that users have a positive experience, regardless of the device they use. Poor mobile responsiveness leads to higher bounce rates, lower engagement, and reduced conversion rates.
How to Assess Mobile Responsiveness:
- Tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test or BrowserStack simulate how your site appears on various mobile devices and screen sizes.
- Ensure that your site uses CSS media queries to adjust the design elements based on the screen size.
- Test interactive elements, such as buttons and links, to ensure they are easily tappable and accessible on mobile devices.
- Assess the load speed of your site on mobile devices, as slow loading times negatively impact user experience.
- Check that the layout adjusts properly, and content such as text, images, and videos are displayed correctly without horizontal scrolling.
Resolve HTTP Errors
HTTP Errors are status codes returned by a web server to indicate that there is a problem with the request or the server itself. Common HTTP errors include 404 (Not Found), 500 (Internal Server Error), and 403 (Forbidden). Resolving HTTP errors is essential for maintaining a functional and user-friendly website. Persistent HTTP errors lead to a poor user experience, as visitors may encounter broken pages or be unable to access content. Additionally, search engines may penalize sites with frequent HTTP errors, negatively impacting search engine rankings and visibility.
How to Resolve HTTP Errors:
- Use tools like Google Search Console or website monitoring tools to identify which HTTP errors are occurring on your site.
- For 404 errors, check and correct broken links or set up proper redirects to guide users to relevant content.
- For 500 errors, check server logs and configurations to diagnose and fix internal server problems.
- For 403 errors, ensure that file permissions and access settings are correctly configured so users and search engines access the content.
- After making fixes, re-test the affected pages to ensure that the errors have been resolved and the pages load correctly.
Renderability Essentials
Renderability refers to a website’s ability to be correctly and fully displayed by web browsers. It involves the successful loading and rendering of all elements on a page, including text, images, and interactive features.
A website that renders properly ensures that visitors access and interact with content seamlessly, which helps retain users and reduces bounce rates. Additionally, proper renderability influences search engine rankings, as search engines favor sites that provide a smooth and accessible experience. Sites that consistently render well are more likely to achieve higher rankings, improve engagement metrics, and enhance overall user satisfaction.
Here are the essentials for ensuring your website’s renderability:
Monitor Server Performance
Server Performance refers to the efficiency and effectiveness with which a server processes requests, manages resources, and delivers content to users. Key metrics include server response times, uptime, CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O. Monitoring server performance is essential for maintaining optimal user experience and operational efficiency. It helps in identifying and resolving issues before they affect users, preventing downtime and service interruptions. Regular performance monitoring also aids in optimizing server resources, ensuring scalability, and enhancing overall system reliability.
How to Monitor Server Performance:
- Use software like New Relic, Datadog, or Nagios to track real-time metrics such as CPU load, memory usage, and network performance.
- Configure alerts for critical thresholds to notify administrators of potential issues like high CPU usage or low disk space before they impact performance.
- Regularly review and analyze server logs to detect and troubleshoot performance anomalies or errors.
- Perform load and stress testing to evaluate how the server handles high traffic and heavy data loads.
- Use uptime monitoring tools to ensure the server is consistently available and to track downtime or outages.
Optimize Load Time and Page Size
Load Time is the duration it takes for a webpage to fully render and become interactive after a user initiates a request. Page Size refers to the total size of all elements on a webpage, including HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, and other media files. Optimizing load time and page size is crucial for providing a better user experience. Faster load times lead to improved user engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates. Reducing page size ensures that pages load efficiently, even on slower connections or mobile devices.
How to Optimize Load Time and Page Size:
- Compress and resize images using tools like TinyPNG or ImageMagick to reduce file sizes without losing quality.
- Reduce the size of CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files by removing unnecessary characters, spaces, and comments using tools like UglifyJS or CSSNano.
- Configure browser caching to store static resources locally, so users don’t need to download them on every visit.
- Distribute content across multiple servers globally to decrease load times by serving files from locations closer to the user.
- Load images and other non-essential content only when they are about to enter the viewport, rather than loading everything up upfront.
- Improve server response times with techniques such as optimizing database queries, upgrading hardware, or using server-side caching.
Ensure JavaScript Renders Properly
JavaScript Rendering Properly refers to the accurate and efficient execution of JavaScript code by a web browser, ensuring that interactive elements, dynamic content, and client-side scripts work as intended. Ensuring that JavaScript renders properly is crucial for providing a seamless user experience. Proper JavaScript execution enables interactive features, dynamic content updates, and smooth user interactions, which are essential for maintaining user engagement and satisfaction. Errors or inefficient scripts lead to broken functionality, slow page performance, and a negative impact on user experience.
How to Ensure JavaScript Renders Properly:
- Verify that your JavaScript code functions correctly on different web browsers and versions to ensure compatibility and consistent performance.
- Implement asynchronous or deferred loading for JavaScript files to prevent blocking the rendering of the webpage and improve load times.
- Regularly check for and fix JavaScript errors using browser developer tools and error logging services to ensure smooth execution.
- Write clean, efficient code and remove unnecessary scripts to enhance performance and reduce the risk of rendering issues.
- Use validation tools and liners to catch syntax errors and code inconsistencies that could affect rendering.
- Use performance monitoring tools to track JavaScript execution times and identify any scripts that may be causing slowdowns or performance bottlenecks.
Identify Orphan Pages
Identifying Orphan Pages involves locating web pages on a site that are not linked to any other page within the same site. These pages are often isolated and only be accessed directly via their URLs. Identifying orphan pages is essential for improving website usability and SEO. Orphan pages are not accessible through regular navigation, which results in lower user engagement and missed opportunities for driving traffic which also helps in optimizing the overall user experience and contributes to better search engine rankings by ensuring that all pages are effectively integrated and accessible.
How to Identify Orphan Pages:
- Tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb crawl your website to generate a list of all pages and highlight those without any internal links.
- Review server logs to identify pages that receive traffic but do not have inbound internal links.
- Compare your sitemap with your internal linking structure to find pages that are listed but not linked from other pages.
- Check the Coverage report and other relevant sections in Google Search Console to identify pages that may not be well-integrated into your site’s structure.
- Search for specific URLs to see if they are accessible and determine if internal links are pointing to them.
Evaluate Page Depth
Evaluating Page Depth involves assessing the number of clicks required to reach a specific webpage from the homepage or other entry points within a website. Page depth measures how far a page is buried within a site’s hierarchy, with fewer clicks indicating shallower depth and more clicks indicating deeper depth. Evaluating page depth is crucial for optimizing site navigation and improving user experience. Pages that are too deep may be difficult for users to find, leading to lower engagement and higher bounce rates. Shallow pages, on the other hand, are easier to access and typically receive more traffic.
How to Evaluate Page Depth:
- Tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb crawl your site and provide a visual representation of your site structure, showing the depth of each page.
- Analyze your website’s hierarchy and menu structure to determine how many levels deep each page is. Ensure that important pages are within a few clicks of the homepage.
- Examine the internal linking structure to see how pages are linked from other pages and how many clicks are needed to access them.
- Track user navigation paths using analytics tools to understand how users access different pages and identify any deep pages that may be hard to reach.
Resolve Redirect Chains
Resolving Redirect Chains involves fixing sequences of multiple redirects that occur when a URL redirects to another URL, which in turn redirects to yet another URL, and so on. Resolving redirect chains is essential for maintaining optimal website performance and user experience. Redirect chains increase page load times, as each redirect adds latency to the user’s journey leading to slower page speeds, higher bounce rates, and lower user satisfaction. Additionally, search engines may struggle to crawl and index pages effectively if they encounter multiple redirects, potentially impacting SEO and search rankings.
How to Resolve Redirect Chains:
- Use site crawling tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to detect redirect chains. These tools highlight URLs that are part of a chain and show the complete redirect path.
- Update your server or CMS configuration to ensure that redirects point directly to their final destination. may involve changing redirect rules or updating links.
- Ensure that internal links point directly to the final URL rather than going through intermediate redirects, which helps in reducing redirect chains.
- Review your redirects to remove any that are outdated or redundant, and ensure that each redirect serves a clear purpose.
- Verify that the redirects are working as intended and that there are no longer any chains by using the same site crawling tools.
Rankability Essentials
Rankability refers to a website’s potential to rank highly on search engine results pages (SERPs) for specific keywords or phrases. It considers factors such as content relevance, domain authority, technical SEO, backlink quality, and user experience. Rankability is crucial for visibility and long-term success in search engines. When a website is optimized for rankability, it attracts more qualified traffic, improves click-through rates (CTR), and enhances brand authority. High rankability also ensures that your content meets search engine algorithms’ criteria, positioning your site competitively against others in your industry.
Here are the key rankability essentials:
Optimize Internal and External Links
Internal Links are hyperlinks that point from one page to another within the same domain. They help users navigate the website and allow search engines to crawl and index pages more effectively. External Links are hyperlinks that point to pages on other domains, providing additional context or resources and often contributing to a website’s authority.
Optimizing internal and external links is crucial for improving a website’s SEO performance and user experience. Internal links help distribute page authority and guide search engines through the site, which boosts rankings and enhances content discoverability. External links build credibility and authority by associating your site with reputable sources, which positively impact search rankings and trustworthiness. Properly managed links also ensure that users find relevant, high-quality content, improving engagement and reducing bounce rates.
How to Optimize Internal and External Links:
1. Internal Links:
- Organize your content into a hierarchical structure and link-related pages to enhance navigation and user experience.
- Ensure that anchor text is relevant and descriptive, helping both users and search engines understand the linked content.
- Regularly check for and fix broken internal links to ensure a smooth user experience and maintain search engine crawl efficiency.
- Direct users to related articles or resources within your site to keep them engaged and reduce bounce rates.
2. External Links:
- Reference high-quality, reputable sites to provide valuable context and enhance your content’s credibility.
- Use external links judiciously to prevent diluting your content’s focus and avoid potential penalties for over-optimization.
- Apply “nofollow” attributes to links that should not pass on ranking credit, such as those in paid ads or user-generated content.
- Regularly audit and update external links to ensure they lead to relevant and functional pages.
Assess Backlink Quality
Backlink Quality refers to the value and relevance of links pointing to your website from other domains. High-quality backlinks come from reputable, authoritative sites and are often considered more valuable than links from low-quality or irrelevant sources. High-quality backlinks from authoritative and relevant sites significantly enhance your site’s credibility, increase search engine rankings, and drive more targeted traffic. Conversely, low-quality or spammy backlinks harm your site’s reputation and rankings. Regularly assessing and managing your backlinks ensures that you build a strong, reputable link profile that supports your overall SEO strategy and long-term success.
How to Assess Backlink Quality:
- Evaluate the linking site’s domain authority or page authority using tools like Moz, Ahrefs, or SEMrush. Higher authority sites generally provide more valuable backlinks.
- Ensure that the linking site’s content is relevant to your own. Relevant links from related industries or topics are more beneficial.
- Analyze the anchor text used for the backlink. Relevant and descriptive anchor text is preferred over generic or unrelated text.
- Consider where the link is placed on the page. Links within the main content or editorial sections are typically more valuable than those in footers or sidebars.
- Look for a diverse range of backlinks from different domains and types of sites to avoid over-reliance on a single source.
Develop Content Clusters
Content Clusters are a strategic SEO approach where related content pieces are grouped around a central “pillar” page, which provides a comprehensive overview of a broader topic. Developing content clusters enhances site organization, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content, which boosts rankings for related keywords. Content clusters also improve user experience by providing a clear, navigable structure, allowing visitors to find comprehensive information on related topics easily. Additionally, the strategy helps establish your site as an authority in specific subject areas, driving more targeted traffic and increasing engagement.
How to Develop Content Clusters:
- Start by defining broad topics relevant to your audience and business. These will serve as the basis for your pillar pages.
- Develop comprehensive, authoritative pages on each core topic. These pages should cover the subject broadly and provide valuable, in-depth information.
- Produce detailed articles or blog posts on specific subtopics related to each pillar page. Ensure that these cluster pages link back to the pillar page and to each other where relevant.
- Use relevant keywords, optimize internal linking, and ensure that both pillar and cluster content are well-structured and user-friendly.
- Regularly review and update your content clusters to maintain relevance and improve search engine rankings.
Clickability Essentials
Clickability, or Click-Through Rate (CTR), is the percentage of users who click on a link or ad after seeing it which measures how appealing a website’s title, meta description, or ad is to the audience. The importance of clickability lies in its direct impact on website traffic and engagement. A higher CTR means more users are interacting with the website or content, which signals relevance to search engines and leads to better rankings. Optimizing for clickability enhances the likelihood of attracting visitors, driving conversions, and ultimately boosting overall performance.
Here are the key Clickability Essentials:
Implement Structured Data
Structured Data is a standardized format used to provide additional context and information to search engines about the content on a webpage. Implementing structured data improves how search engines interpret your content, leading to enhanced search results like rich snippets or featured snippets. The added visibility increases the chances of attracting user clicks, improving click-through rates (CTR), and driving more organic traffic. Structured data also helps make your content eligible for special search features, giving you a competitive edge in search engine results pages (SERPs).
How to Implement Structured Data:
- Choose the right schema type for your content (e.g., products, articles, events) using resources like Schema.org.
- Use JSON-LD, Microdata, or RDFa formats to embed structured data into your webpage’s HTML.
- Validate the structured data with Google’s Rich Results Test or Schema Markup Validator to ensure it’s error-free.
- Monitor performance using Google Search Console to see how search engines interpret the structured data.
Achieve SERP Features
SERP Features are enhanced search results on the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) that go beyond the traditional blue links, such as featured snippets, rich snippets, knowledge panels, image packs, and local packs. Achieving SERP features is crucial as they capture prime real estate on search result pages, often appearing above organic results that significantly increase visibility and click-through rates, driving more traffic to your website. SERP features provide quick, valuable information to users, positioning your site as a trusted authority in the eyes of both search engines and visitors, which leads to better engagement, brand credibility, and higher conversions.
How to Achieve SERP Features:
- Use clear, concise answers to commonly asked questions, organize content with headers, and provide structured information.
- Use schema markup (e.g., for reviews, products, or FAQs) to help search engines better understand your content and qualify for rich snippets.
- Ensure your site is technically optimized with fast load times, mobile-friendliness, and high-quality content.
- Create content that addresses what users are searching for, including how-to guides, FAQs, and comparison posts.
- For businesses with a physical presence, use Google My Business and local keywords to appear in local packs.
Optimize for Featured Snippets
Featured Snippets are concise excerpts of information that appear at the top of Google’s search results, often referred to as “Position Zero “ which provide users with quick answers to their queries and are in the form of paragraphs, lists, or tables. Optimizing for featured snippets is essential because it increases your content’s visibility by placing it in a highly prominent position above traditional search results that drive more organic traffic, improve click-through rates (CTR), and establish your site as an authoritative source. Featured snippets also improve brand credibility and help capture users who are seeking quick answers, thereby increasing engagement and potentially boosting conversions.
How to Optimize for Featured Snippets:
- Identify common questions related to your topic and answer them concisely in the content. Aim for a direct, well-structured response within 40-60 words.
- Organize your content with clear headings that highlight questions or topics, making it easy for search engines to extract relevant information.
- Focus on long-tail, question-based keywords (e.g., “How to,” “What is”) that often trigger featured snippets.
- Structure content into bullet points or tables, as featured snippets frequently show lists or comparison data.
- Although structured data is not a direct requirement for featured snippets, implementing it helps search engines better understand your content, increasing the chances of snippet eligibility.
Consider Google Discover
Google Discover is a personalized content feed that delivers articles, videos, and other relevant content to users based on their interests, search history, and online behavior. Google Discover is vital because it allows your content to reach users before they even perform a search, creating a passive way to drive traffic that significantly increases visibility and engagement by presenting your content directly to users who are likely to be interested. With its personalized approach, Google Discover helps build brand awareness, capture new audiences, and increase the longevity of content by continually surfacing it to relevant users.
How to Consider Google Discover:
- Focus on high-quality, relevant content that stays valuable over time and aligns with users’ interests.
- Google Discover often highlights content with visually appealing images. Use large, high-resolution images to increase your chances of being featured.
- Ensure your site is mobile-friendly, as Discover is primarily a mobile feature.
- Produce content that establishes credibility and trust, as Google Discover favors authoritative sources.
- Publish content on topics that are gaining traction and align with your audience’s interests, as Discover surfaces trending news and stories.
Relevant Content from Matt EMGI
HARO Link Building Become the Go-To Expert in Your Industry Strategic HARO outreach that positions you as an industry authority while securing high-DR editorial links from top publications. Schedule a Call Expert Responses Professionally crafted responses to journalists High-DR Publications
Ecommerce Link Building Drive More Sales Through Strategic Links Specialized link building for ecommerce brands. Product placements, category pages, and brand authority links that drive both traffic and sales. Schedule a Call Sales-Focused Links that drive actual product sales Category
SaaS Link Building Dominate SaaS Search Results Strategic link building for SaaS companies. High-authority and mega contextual links from tech industry blogs, SaaS companies and even the unicorns. We landed links on Zoom, Hubspot and BigCommerce for multiple clients. Schedule
Scalable rankings, traffic, authority & REVENUE Backlinks that FUEL Silly Growth Results within 45 days, NOT 18 months Schedule a Call Why Choose EMGI Group? We’re authoritative, but trying new things. Modern and tech-first, not stuck in the old ways.